In normal publish-subscribe operations, a message is published to all RTclients subscribing to the subject to which the message is being sent. However, in some situations you may wish to have messages sent to only one of a specified set of RTclients. An example of this is a project where there is high message throughput and each message takes some time to process. In this case, you may wish to replicate a set of RTclients and have them take turns processing (or have the least busy one handle) the messages to better keep up with message flow.
This is accomplished in SmartSockets with load balancing. Rather than have a single RTclient handle all the messages, you can use load balancing to process the messages across multiple RTclients. This is very useful when processing a heavy message load. A load-balanced message is routed to only a single RTclient, not to all RTclients subscribed to the destination subject. The RTclient to which the message is routed is selected based on the load balancing mode specified. Load balancing implies that there is a set of RTclients that are all equally capable of processing load-balanced messages.
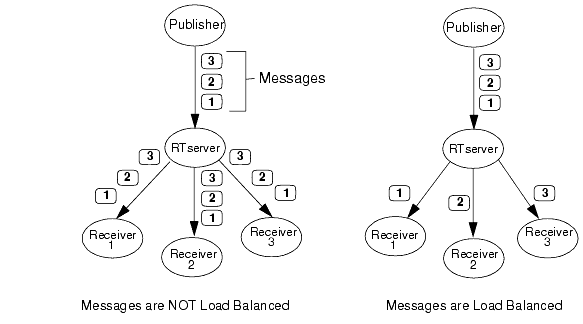
For example, consider the simple example shown in Figure 4. There are three receivers, all subscribed to the same subject. Messages 1, 2, and 3 are published to that subject. On the left side of the figure, each message is routed to all receivers because there is no load balancing. The right side shows what happens when the messages are marked to be delivered using round-robin load balancing. The first message is delivered to Receiver 1, the second message to Receiver 2, and the third message to Receiver 3. Each message is delivered to only a single RTclient.

Load balancing can be specified on a per-message basis or per-message-type basis through the load balancing mode message property. Load balancing is dynamic in that whenever an RTclient connects to or disconnects from RTserver, the load balancing calculations are updated in real time. When an RTclient publishes the first message using load balancing to a subject, RTserver starts collecting subject subscription information from the appropriate other RTservers to accurately track load balancing accounting. This increases the scalability of load balancing because only the relevant RTservers dynamically exchange load balancing information.
By default, messages are not load balanced and are distributed to all subscribers. Setting the load balance mode per message takes precedence over message type. Setting load balancing for a message type takes precedence over the default value of TipcDefs.LB_NONE.
SmartSockets supports four load balancing modes:
|
TipcDefs.LB_NONE
|
is the default and specifies no load balancing. The message is sent to all subscribers.
|
|
TipcDefs.LB_ROUND_ROBIN
|
specifies that the list of subscribing RTclients is held in a circular list, with each successive message simply sent to the next RTclient in the list (as shown in Figure 4). This mode is a good choice when the subscribers are all capable of receiving and processing a request with nearly equal speed. There is no additional overhead with this mode.
|
|
TipcDefs.LB_WEIGHTED
|
specifies that the message is published to the RTclient that has the fewest pending requests. This mode is a good choice when the subscribers differ significantly in their ability to process a request promptly, due to, for example, hardware speed or network delays. This method can only be used with GMD and requires no additional overhead beyond what GMD requires.
|
|
TipcDefs.LB_SORTED
|
specifies that the message is always sent to the first RTclient in the list. The list is formed by doing an alphabetical sort of the unique subject name of each RTclient. This mode is a good choice when you want a specific subscriber to process all messages until it fails, when a hot standby can take over. There is no additional overhead with this mode.
|
For further information on load balancing, refer to the TIBCO SmartSockets User’s Guide.
|
TIBCO SmartSockets™ Java Library User’s Guide and Tutorial Software Release 6.8, July 2006 Copyright © TIBCO Software Inc. All rights reserved www.tibco.com |